Git
Version Control System (VCS)
Basic Concepts
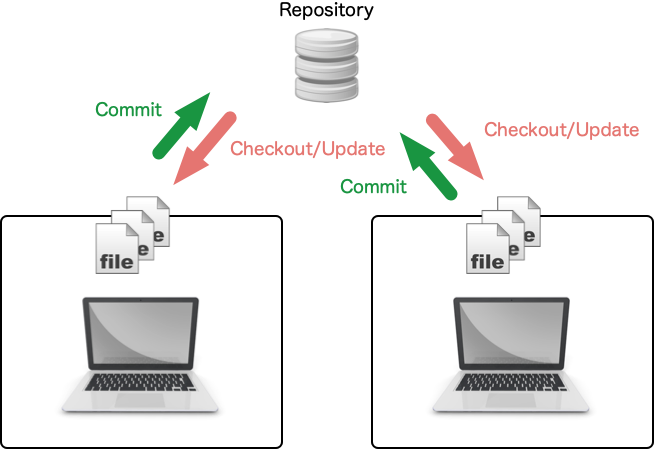
- Repository: A database to store artifacts of development
- Data: Source codes, specifications (documents), test codes, etc.
- History of changes
- Checkout: Load a specific version in the repository to local files
- Commit: Save local files to the repository (the change history is saved)
Advanced Concepts
Conflict
- Data integrity
- All the changes are properly applied
- File lock is the simplest way to gurantee the data integrity
- Conflict
- The same position have been changed by two or more users.
- The history of changes is undetermined.
- The conflict should be resolved by hands.
Branch and Merge
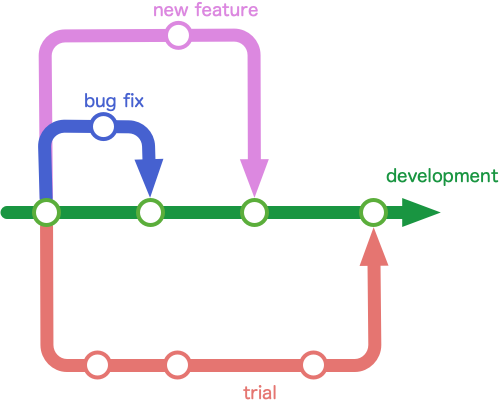
What is branch
- A branch is a stream of history of changes, the management unit in the repository
- a branch for development, a branch for releases, a branch for debugging, etc.
How to use
- Making a new branch from the present branch
- Merging changes on a branch to another branch
Why
- There is no conflict between different branches.
- The conflict is caused by merging branches.
Git
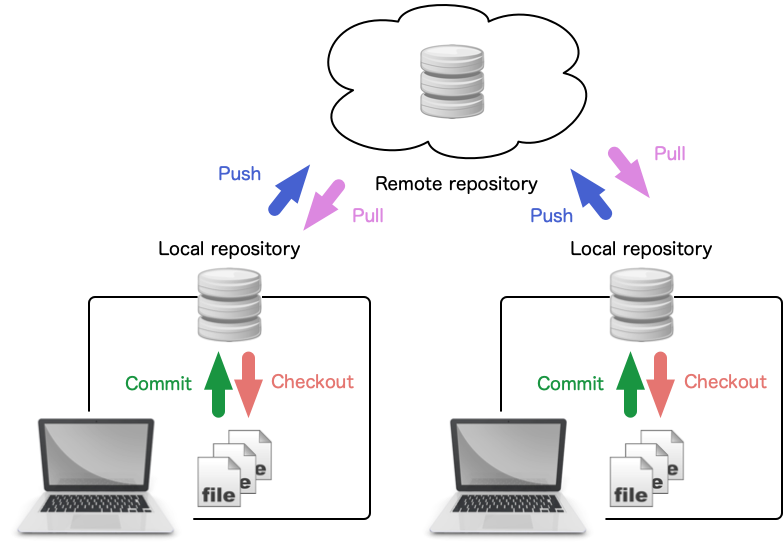
- A distributed version control system
- This is originally developed on SCM for Linux.
- Two repositories
- Remote repository located in a server
- Local repository located in a client (local PC)
- Basic Operations
- clone: copy a remote repository to a local repository
- commit: save history of changes to the local repository
- push: update the remote repository by the local repository
- pull: update the local repository by the remote repository
- Default branch name:
main (master)
Usage
git xxxx where xxxx is a mode of git command
Basic commands
git clone: Copy a remote repository to a local repositorygit checkout: Checkout a branch from the local repository (change a branch)git add: Add files to stage as files to be committedgit commit: Save the history to the local repositorygit status: Display the status of the local repositorygit branch: Display branches of the local repositorygit log: Display the commit loggit push: Update the remote repository by the local repositorygit pull: Update the local repository by the remote repository
Basic Flow
- Create a local repository (only once at the beginning)
- Update the local repository with the remote repository
- Checkout the files from the local repository
- Edit the files
- Add the editted files to a stage
- Commit the history of files that are added to the stage
- (Repeat Step 4 through Step 6)
- Update the remote repository with the local repository
Basic Flow
- Create a local repository (only once at the beginning) git clone, git init
- Update the local repository with the remote repository git pull
- Checkout the files from the local repository git checkout, git branch
- Edit the files
- Add the editted files to a stage git add, git status
- Commit the history of files that are added to the stage git commit, git log
- (Repeat Step 4 through Step 6)
- Update the remote repository with the local repository git push
Summary
- Version Control System (VCS)
- Repository, Checkout, Commit
- Conflict, Branch, Merge
- Git
- Distributed VCS
- Remote repository, Local repository
- Basic commands: clone, checkout, add, commit, status, branch, log, push, pull
- Basic flow of Git
- Create a local repository, Update the local repository, Checkout files, Edit files, Add files to stage, Commit history, Update the remote repository


